 |
Another representation used by some algorithms is given by the
chained lists .
This representation uses four vectors,
fe, che, fn and chn which are
described below:
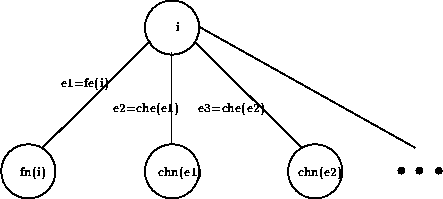
e1=fe(i)) is the number of the first edge starting from node
i
e2=che(e1) is the number of the second edge starting from
node i
e3=che(e2) is the number of the third edge starting from
node i
and so on until the value is 0
fn(i) is the number of the first node reached from node i
chn(i) is the number of the node reached by edge
che(i).
All this can be more clearly seen on figure 2.
You can use the chain_struct function to obtain the chained lists representation of a graph from the adjacency lists representation (see 1.2.3).