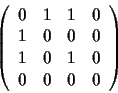The ![]() node-node
matrix of the
graph is the matrix A where A(i,j)=1 if there is one arc from node i to
node
j. Only 1 to 1
graphs (no more than one arc from one node to another) can be
represented, but loops are allowed.
This matrix is also known as the ``adjacency matrix''.
node-node
matrix of the
graph is the matrix A where A(i,j)=1 if there is one arc from node i to
node
j. Only 1 to 1
graphs (no more than one arc from one node to another) can be
represented, but loops are allowed.
This matrix is also known as the ``adjacency matrix''.
The same functions used to compute the node-arc matrix (see above) of a graph are used to compute the node-node matrix: graph_2_mat and mat_2_graph. To specify that we are working with the node-node matrix, the flag 'nodenode' must be given as the last argument of these functions.
For instance, you can find below the node-node matrix of the graph
corresponding to Figure 1:
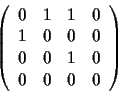
and the node-node matrix for the same undirected graph: