According to UNAIDS estimates, around 2.3 million people were living with HIV in Europe at the end of 2008.1 Estimated HIV prevalence varies from below 0.1% in parts of Central Europe to above 1% in parts of the former Soviet Union.
The three main tables in this page have been constructed from estimates from the 2008 UNAIDS report on the global AIDS epidemic. Unless stated otherwise, all other data is from the 2008 HIV/AIDS surveillance report by the European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC) and World Health Organisation Regional Office for Europe.
As a large number of HIV infections, AIDS cases, and AIDS deaths are never reported at a national level, the figures from the ECDC/WHO report understate the true extent of the epidemic. In addition, the reliability of reporting systems varies between countries, making comparisons difficult.
Regional summary
As the graph below shows, rates of newly diagnosed cases of HIV infection vary widely between Eastern, Central and Western Europe.
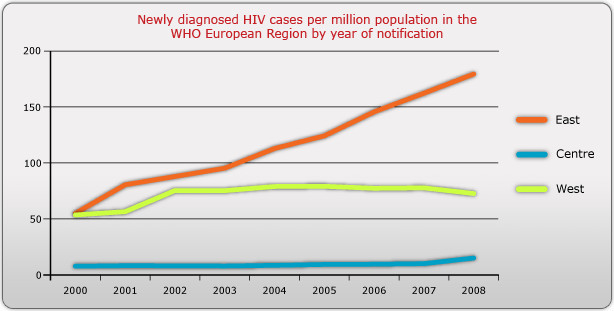
Eastern Europe has seen a steady increase in HIV infections since 2000, which is largely due to an increase in heterosexually acquired infections and infections among injecting drug users.
The graph below shows how the rate of reported AIDS diagnoses in Eastern Europe has also increased in recent years.
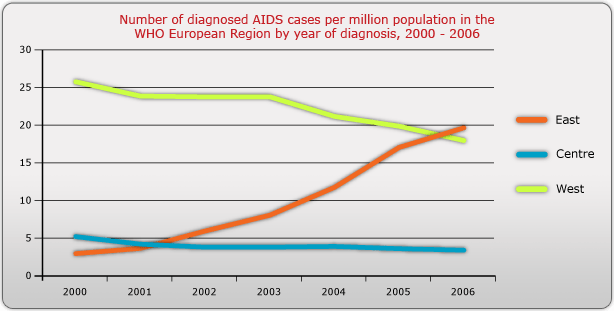
The number of AIDS cases per million population has declined slightly in Western and Central Europe. This is largely a result of the widespread availability of antiretroviral drugs in this region. Find out more about HIV and AIDS in Western and Central Europe.
Western Europe
| Western European country | People living with HIV/AIDS 2007 | Adult prevalence % 2007 | Women with HIV/AIDS 2007 | AIDS deaths 2007 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Andorra | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| Austria | 9,800 | 0.2 | 2,900 | ... |
| Belgium | 15,000 | 0.2 | 4,100 | <100 |
| Denmark | 4,800 | 0.2 | 1,100 | ... |
| Finland | 2,400 | 0.1 | <1,000 | ... |
| France | 140,000 | 0.4 | 38,000 | 1,800 |
| Germany | 53,000 | 0.1 | 15,000 | <500 |
| Greece | 11,000 | 0.2 | 3,000 | <100 |
| Iceland | <500 | 0.2 | <200 | ... |
| Ireland | 5,500 | 0.2 | 1,500 | <100 |
| Israel | 5,100 | 0.1 | 2,900 | <200 |
| Italy | 150,000 | 0.4 | 41,000 | 1,900 |
| Luxembourg | ... | 0.2 | <200 | ... |
| Malta | <500 | 0.1 | ... | ... |
| Monaco | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| Netherlands | 18,000 | 0.2 | 4,900 | <200 |
| Norway | 3,000 | 0.1 | <1,000 | ... |
| Portugal | 34,000 | 0.5 | 9,400 | <500 |
| San Marino | ... |
... | ... | ... |
| Spain | 140,000 | 0.5 | 28,000 | 2,300 |
| Sweden | 6,200 | 0.1 | 2,900 | <100 |
| Switzerland | 25,000 | 0.6 | 9,200 | <500 |
| United Kingdom | 77,000 | 0.2 | 22,000 | <500 |
HIV statistics
A cumulative total of 318,233 HIV infections had been diagnosed in Western Europe by the end of 2008. This considerably understates the true figure because not all HIV infections have been diagnosed or reported. This is partly because many people do not know that they are infected. In addition, the three countries with the most extensive epidemics either do not report from all regions (Italy and Spain) or started reporting only in 2003 (France and Spain). National HIV reporting started at different dates in different countries, without systematic retrospective reporting of infections diagnosed in previous years.
Of the reported 24,296 people diagnosed with HIV in Western Europe in 2008:
- 42% probably acquired HIV through heterosexual contact;
- 35% were men who had sex with men;
- 4% were injecting drug users;
- 30% were female;
- and 10% were 15 to 24 years old.
When looking at diagnoses in the 15 Western countries that have consistently reported data since 2000, the number of cases has increased from 12,015 in 2000 to 16,657 in 2008. This is an increase from 53 HIV diagnoses per million population to 72 per million. Countries with the highest rates in 2008 were San Marino (130.8/million), the United Kingdom (119.3/million) and Portugal (105.9/million). Although Italy does not have a national monitoring system for new HIV diagnoses, regional reporting shows HIV incidence in 2007 was as high as 145/million in the Province of Rimini.2
Data on the original country in which infection occurred is available for 15 countries. According to these data, 38% of infections reported in 2008 originated from the country of report, and 19% were acquired in sub-Saharan Africa. Latin America and the Caribbean, and other countries in Western Europe accounted for 4% each. The origin was undetermined for nearly a quarter of cases.
AIDS statistics
In 2008 there were 4724 diagnosed cases of AIDS reported in 19 of the countries in the West. The highest rates of AIDS diagnoses were in Portugal (36.4/million), Spain (29.1/million), Malta (19.5/million) and Italy (17.2/million).
After falling dramatically in the late 1990s (following the introduction and widespread use of combination antiretroviral treatment), AIDS incidence has declined steadily. The number of AIDS diagnoses in 2008 was 55% lower than that for 2000.
AIDS mortality has also decreased as antiretroviral therapy has become widely available. Far fewer people died of AIDS in 2008 (1,303) than in 2003 (2,986).
Central Europe
| Central European country | People living with HIV/AIDS 2007 | Adult prevalence % 2007 | Women with HIV/AIDS 2007 | AIDS deaths 2007 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Albania | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| Bosnia & Herzegovina | <500 | <0.1 | ... | ... |
| Bulgaria | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| Croatia | <500 | <0.1 | ... | ... |
| Cyprus | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| Czech Republic | 1,500 | ... | <500 | ... |
| Hungary | 3,300 | 0.1 | <1,000 | ... |
| Macedonia, F.Y.R. | <500 | <0.1 | ... | ... |
| Montenegro | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| Poland | 20,000 | 0.1 | 5,500 | <200 |
| Romania | 15,000 | 0.1 | 7,000 | ... |
| Serbia | 6,400 | 0.1 | 1,800 | <100 |
| Slovakia | <500 | <0.1 | ... | ... |
| Slovenia | <500 | <0.1 | ... | <100 |
| Turkey | ... | ... | ... | ... |
HIV statistics
There were a total of 1,762 HIV diagnoses in Central Europe in 2008, only a slight increase since 2000. Of these diagnoses, 19% were in individuals aged 15 to 24 years old and 22% were female. Of those infections where the transmission route was known:
- 19% were acquired through heterosexual contact (only 3% of these were in persons from countries with generalised epidemics);
- 27% were among men who have sex with men;
- and 7% were among injecting drug users.
Patterns vary, however, with heterosexual sex accounting for the majority of new infections in Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Romania and Macedonia F.Y.R., and men who have sex with men accounting for the majority in Czech Republic, Hungary, Serbia, Slovenia, Slovakia and Croatia.
AIDS statistics
In 2008, 530 cases of AIDS were reported, just over half of those reported in 2000. This decrease reflects the widespread availability of antiretroviral therapy in the region. The highest rates of AIDS cases were reported in Romania (10/million).
In 2008 there were a reported 209 AIDS deaths in Central Europe, compared to 359 in 2004.
Eastern Europe
| Eastern European country | People living with HIV/AIDS 2007 | Adult prevalence % 2007 | Women with HIV/AIDS 2007 | AIDS deaths 2007 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Armenia | 2,400 | 0.1 | <1,000 | <200 |
| Azerbaijan | 7,800 | 0.2 | 1,300 | <100 |
| Belarus | 13,000 | 0.2 | 3,900 | <1,000 |
| Estonia | 9,900 | 1.3 | 2,400 | <500 |
| Georgia | 2,700 | 0.1 | <1,000 | ... |
| Kazakhstan | 12,000 | 0.1 | 3,300 | <500 |
| Kyrgyzstan | 4,200 | 0.1 | 1,100 | ... |
| Latvia | 10,000 | 0.8 | 2,700 | <500 |
| Lithuania | 2,200 | 0.1 | <1,000 | <200 |
| Republic of Moldova | 8,900 | 0.4 | 2,600 | <100 |
| Russian Federation | 940,000 | 1.1 | 240,000 | 35,000 |
| Tajikistan | 10,000 | 0.3 | 2,100 | <100 |
| Turkmenistan | <500 | <0.1 | ... | ... |
| Ukraine | 440,000 | 1.6 | 190,000 | 19,000 |
| Uzbekistan | 16,000 | 0.1 | 4,600 | <500 |
HIV statistics
In 2008 in Eastern Europe there were a reported 25,542 newly diagnosed HIV infections. However, this number does not include figures from the Russian Federation, where nearly 55,000 new HIV cases were reported in 2008. The Ukraine has the second highest number of annual infections; in 2008 15,671 were reported. However, these figures do not represent the true extent of the epidemic. UNAIDS estimates that 110,000 people became infected with HIV in 2007, and of the 1.5 million people living with HIV in the region, around 90 percent live in either the Russian Federation (69%) or the Ukraine (29%).
Of the new HIV diagnoses in 2008 (where data on transmission routes were available):
- 45% resulted from injecting drug use;
- 44% were acquired through heterosexual transmission;
- 0.5% were men who had sex with men;
- 15% were aged 15-24 years;
- and 41% were female.
In addition to the Russian Federation and the Ukraine, high rates of HIV are reported in Estonia (406/million) and the Republic of Moldova (219/million). Rates of newly diagnosed HIV infections have generally declined in Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania, but in Armenia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Azerbaijan and Tajikistan rates have significantly increased since 2003/4.
AIDS statistics
A total of 2,311 AIDS diagnoses were reported in 2008 in Eastern Europe. However, this figure significantly underestimates the actual number, due to reporting delays and incomplete data from a number of countries (including the Russian Federation). In fact, UNAIDS estimated that in the same year, some 87,000 people died of AIDS in this region.3 Nearly all countries providing data since 2000 have seen an increase in the number of AIDS diagnoses.
Where Next?
AVERT.org has more about:
Page amended by Gemma Spink.
References:
- UNAIDS (2009), 'AIDS Epidemic Update'
- Ministero del Lavoro, della Salute e delle Politiche Sociali (2007) ‘Dati Epidemiologici’
- UNAIDS (2009), 'AIDS Epidemic Update'
Sources:
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control/WHO Regional Office for Europe (2009) 'HIV/AIDS surveillance in Europe 2008'
- UNAIDS (2008) 'Report on the global AIDS epidemic'


 SIDA y VIH
SIDA y VIH