An R package that provides functionality to fit and simulate from stationary vine copula models for time series.
The package is build on top of rvinecopulib and univariateML.
Install the development version from Github.
# install.packages("remotes")
remotes::install_github("tnagler/svines")For detailed documentation and examples, see the API documentation.
library(svines)
#> Loading required package: rvinecopulib
data(returns) # data set of stock returns
returns <- returns[1:500, 1:2]fit <- svine(returns, p = 1) # Markov order 1
#> Warning in f(x, na.rm = na.rm): The iteration limit (iterlim = 100) was reached
#> before the relative tolerance requirement (rel.tol = 0.0001220703125).
#> Warning in f(x, na.rm = na.rm): The iteration limit (iterlim = 100) was reached
#> before the relative tolerance requirement (rel.tol = 0.0001220703125).
summary(fit)
#> $margins
#> # A data.frame: 2 x 5
#> margin name model parameters loglik
#> 1 Allianz Skew Student-t 0.00039, 0.01589, 5.45534, 0.91785 1382
#> 2 AXA Skew Student-t 0.00052, 0.02089, 4.35198, 0.90611 1260
#>
#> $copula
#> # A data.frame: 5 x 10
#> tree edge conditioned conditioning var_types family rotation parameters df
#> 1 1 3, 2 c,c t 0 0.037, 4.893 2
#> 1 2 2, 1 c,c t 0 0.86, 3.48 2
#> 2 1 4, 2 3 c,c joe 90 1.1 1
#> 2 2 3, 1 2 c,c indep 0 0
#> 3 1 4, 1 2, 3 c,c t 0 0.079, 8.994 2
#> tau
#> 0.023
#> 0.662
#> -0.033
#> 0.000
#> 0.051contour(fit$copula)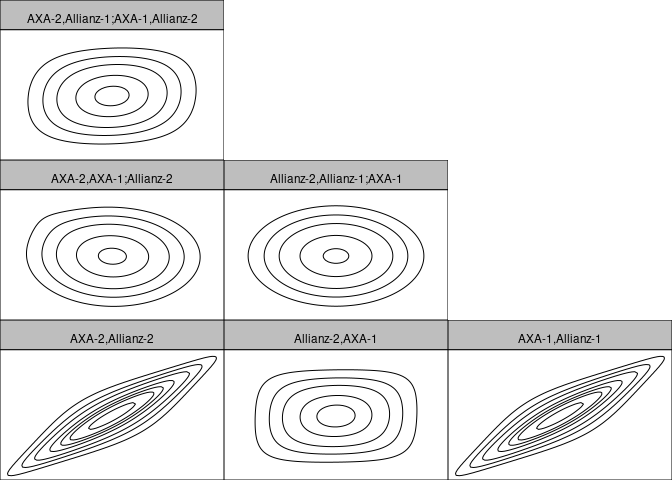
svine_sim() can be used in two different ways:
sim <- svine_sim(n = 500, rep = 1, model = fit)
pairs(sim)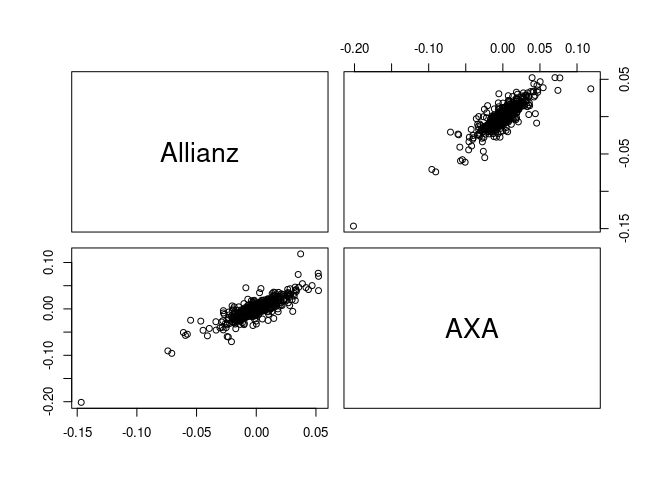
pairs(returns)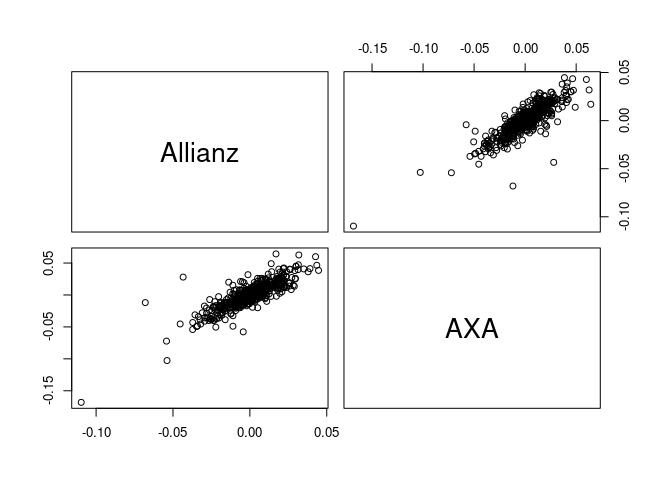
sim <- svine_sim(n = 1, rep = 100, model = fit, past = returns)
pairs(t(sim[1, , ]))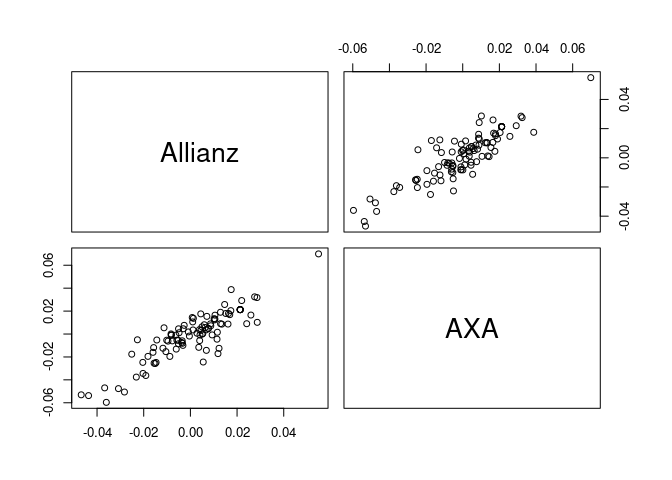
To generate new bootstrapped models from the asymptotic distribution, use
models <- svine_bootstrap_models(2, fit)
summary(models[[1]])
#> $margins
#> # A data.frame: 2 x 5
#> margin name model parameters loglik
#> 1 Allianz Skew Student-t 0.0013, 0.0152, 6.6989, 0.9363 NA
#> 2 AXA Skew Student-t 0.0021, 0.0191, 5.8851, 0.9247 NA
#>
#> $copula
#> # A data.frame: 5 x 10
#> tree edge conditioned conditioning var_types family rotation parameters df
#> 1 1 3, 2 c,c t 0 0.018, 4.545 2
#> 1 2 2, 1 c,c t 0 0.87, 3.31 2
#> 2 1 4, 2 3 c,c joe 90 1.1 1
#> 2 2 3, 1 2 c,c indep 0 0
#> 3 1 4, 1 2, 3 c,c t 0 0.11, 9.70 2
#> tau
#> 0.012
#> 0.674
#> -0.059
#> 0.000
#> 0.070
summary(models[[1]])
#> $margins
#> # A data.frame: 2 x 5
#> margin name model parameters loglik
#> 1 Allianz Skew Student-t 0.0013, 0.0152, 6.6989, 0.9363 NA
#> 2 AXA Skew Student-t 0.0021, 0.0191, 5.8851, 0.9247 NA
#>
#> $copula
#> # A data.frame: 5 x 10
#> tree edge conditioned conditioning var_types family rotation parameters df
#> 1 1 3, 2 c,c t 0 0.018, 4.545 2
#> 1 2 2, 1 c,c t 0 0.87, 3.31 2
#> 2 1 4, 2 3 c,c joe 90 1.1 1
#> 2 2 3, 1 2 c,c indep 0 0
#> 3 1 4, 1 2, 3 c,c t 0 0.11, 9.70 2
#> tau
#> 0.012
#> 0.674
#> -0.059
#> 0.000
#> 0.070Nagler, T., Krüger, D., Min, A. (2022). Stationary vine copula models for multivariate time series. Journal of Econometrics, 227(2), pp. 305-324 [pdf] [doi]