passport smooths the process of working with country
names and codes via powerful parsing, standardization, and conversion
utilities arranged in a simple, consistent API. Country name formats
include multiple sources including the Unicode CLDR common-sense
standardizations in hundreds of languages.
Install from CRAN with
install.packages("passport")or the development version from GitHub with
# install.packages("remotes")
remotes::install_github("alistaire47/passport")Working with country data can be frustrating. Even with well-curated
data like gapminder,
there are some oddities:
library(passport)
library(gapminder)
library(dplyr) # Works equally well in any grammar.
library(tidyr)
set.seed(47)
grep("Korea", unique(gapminder$country), value = TRUE)
#> [1] "Korea, Dem. Rep." "Korea, Rep."
grep("Yemen", unique(gapminder$country), value = TRUE)
#> [1] "Yemen, Rep."passport offers a framework for working with country
names and codes without manually editing data or scraping codes from
Wikipedia.
If data has non-standardized names, standardize them to an ISO 3166-1
code or other standardized code or name with
parse_country:
gap <- gapminder %>%
# standardize to ISO 3166 Alpha-2 code
mutate(country_code = parse_country(country))
gap %>%
select(country, country_code, year, lifeExp) %>%
sample_n(10)
#> # A tibble: 10 x 4
#> country country_code year lifeExp
#> <fct> <fct> <int> <dbl>
#> 1 France FR 2002 79.6
#> 2 Ireland IE 1997 76.1
#> 3 Honduras HN 1982 60.9
#> 4 Iran IR 1967 52.5
#> 5 Central African Republic CF 1972 43.5
#> 6 Madagascar MG 1997 55.0
#> 7 Albania AL 1952 55.2
#> 8 Jamaica JM 2002 72.0
#> 9 Philippines PH 1997 68.6
#> 10 Libya LY 1972 52.8If country names are particularly irregular, in unsupported
languages, or are even just unique location names,
parse_country can use Google Maps or Data Science Toolkit
geocoding APIs to parse instead of regex:
parse_country(c("somewhere in Japan", "日本", "Japon", "जापान"), how = "google")
#> [1] "JP" "JP" "JP" "JP"
parse_country(c("1600 Pennsylvania Ave, DC", "Eiffel Tower"), how = "google")
#> [1] "US" "FR"If data comes with countries already coded,
as_country_code()as_country_name()as_country_name()# NATO member defense expenditure data; see `?nato`
data("nato", package = "passport")
nato %>%
select(country_stanag) %>%
distinct() %>%
mutate(
country_iso = as_country_code(country_stanag, from = "stanag"),
country_name = as_country_name(country_stanag, from = "stanag", short = FALSE),
country_name_thai = as_country_name(country_stanag, from = "stanag", to = "ta-my")
)
#> # A tibble: 29 x 4
#> country_stanag country_iso country_name country_name_thai
#> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr>
#> 1 ALB AL Albania அல்பேனியா
#> 2 BEL BE Belgium பெல்ஜியம்
#> 3 BGR BG Bulgaria பல்கேரியா
#> 4 CAN CA Canada கனடா
#> 5 CZE CZ Czechia செசியா
#> 6 DEU DE Germany ஜெர்மனி
#> 7 DNK DK Denmark டென்மார்க்
#> 8 ESP ES Spain ஸ்பெயின்
#> 9 EST EE Estonia எஸ்டோனியா
#> 10 FRA FR France பிரான்ஸ்
#> # … with 19 more rowsLanguage formats largely follow IETF language tag
BCP 47 format. For all available formats, run
DT::datatable(codes) for an interactive widget of format
names and further information.
A particularly common hangup with country data is presentation. While “Yemen, Rep.” may be fine for exploratory work, to create a plot to share, such names need to be changed to something more palatable either by editing the data or manually overriding the labels directly on the plot.
If the existing format is already standardized, passport
offers another option: use a formatter function created with
country_format, just like for thousands separators or
currency formatting. Reorder simply with
order_countries:
library(ggplot2)
living_longer <- gap %>%
group_by(country_code) %>%
summarise(start_life_exp = lifeExp[which.min(year)],
stop_life_exp = lifeExp[which.max(year)],
diff_life_exp = stop_life_exp - start_life_exp) %>%
top_n(10, diff_life_exp)
#> `summarise()` ungrouping output (override with `.groups` argument)
# Plot country codes...
ggplot(living_longer, aes(x = country_code, y = stop_life_exp - 3.3,
ymin = start_life_exp,
ymax = stop_life_exp - 3.3,
colour = factor(diff_life_exp))) +
geom_point(pch = 17, size = 15) +
geom_linerange(size = 10) +
# ...just pass `labels` a formatter function!
scale_x_discrete(labels = country_format(),
# Easily change order
limits = order_countries(living_longer$country_code,
living_longer$diff_life_exp)) +
scale_y_continuous(limits = c(30, 80)) +
labs(title = "Life gets better",
subtitle = "Largest increase in life expectancy",
x = NULL, y = "Life expectancy") +
theme(axis.text.x = element_text(angle = 30, hjust = 1),
legend.position = "none")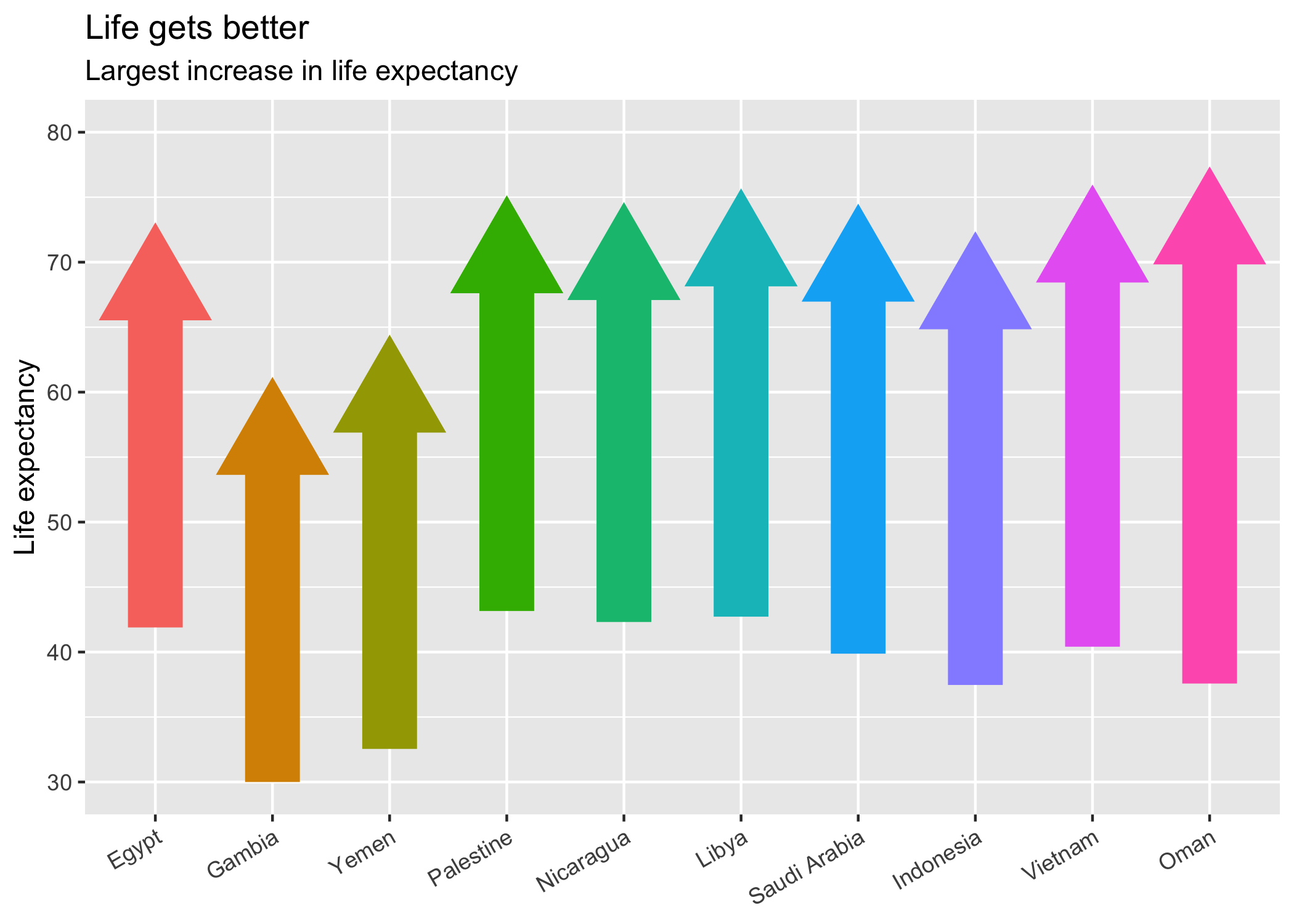
By default country_format will use Unicode CLDR (see
below) English names, which are intelligible and suitable for most
purposes. If desired, other languages or formats can be specified just
like in as_country_name.
The data underlying passport comes from a number of
sources, including
parse_country() are from countrycode.
If you would like to improve both packages, please contribute regex
there!passport is licensed as open-source software under GPL-3. Unicode CLDR
data is licensed according to its
own license, a copy of which is included. countrycode
regex are used as a modification under GPL-3; see the included
aggregation script for modifying code and date.